Reference models - Model of the PSTN/ISDN network
Implementation: PSTN ISDN VoIP subnetwork of the test network.
The PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) - (circuit, line) switched public network is one of the oldest technologies, but in details it is used even in today. Nodes of this network are generated by switching exchanges connected with trunks and its terminals are generated by subscriber terminals (telephone sets). At the beginning network provided only a telephone service (its name was POTS Plain Old Telephone Services).
Later the ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) was built to this network with change of the elements of the network. ISDN allows transmission of data, data packets, picture, fax and other news materials besides speech through a digital subscriber access (partly with line switching, partly with packet switching), thus it can provide a service of a higher quality to the subscribers. This network realizing classic services is called today "narrowband network".
Definitions:
- Channel: (Circuit) is a subset, which connects the two terminals of transmitting route. Channel realizes service between the terminals.
Reference: Chapter 6 of [7]
Channels can be classified on the basis of the forwarded electric signals:
- analogue channel ( a continuous-time signal with a continuous set of values)
- digitális csatorna ( a discrete-time (sampled) signal with a discrete set of values (quantized))
If bandwidth of the news transmittable through the channel is smaller, than bandwidth of the channel, then channel can be shared, ie. we can forward several news materials through the same channel.
(Reference: Chapter 13 of [7])
Processes of the division of channel:
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- restricted time division (rotary) (acronym "TDM" is often used for this process)
- flexible time division (packet switching)
- polling
- random access (Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA)
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- Telephone channel : This channel is used primarily for speech transmission. Bandwidth of the analogue channel is 3,1 kHz (300-3400Hz), and "bandwidth" of the digital channel is 64 kbit/s (8 kHz, 8 bit)
- Transmission route, Trunk, (Link, Path): aggregation of lines, circuits with the same features
- Terminal: Equipment handled by users of the network (telephones, faxes, modems, etc.)
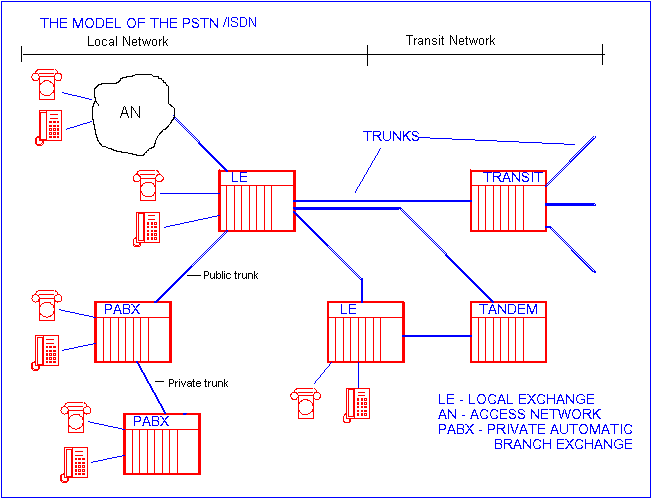
- Local (Subscriber) network: - Local Network - terminals + transmission medium (cable network + digital subscriber transmission systems) + AN + LE
Its parts :
- Local Exchange (LE): It provides direct or indirect (access network) connection for subscriber terminals to the public network.
- Private Automatic Branch Exchange(PABX, PBX): It provides connection for a large amount of private terminals (e.g. institutes) to the public network.
- Access Network (AN): A network between the subscriber device and the local exchange.
Its elements:
outplaced switch grades of the local exchanges, line extension chords, subexchanges (PBXs), which provide economical connections for a large amount of remote terminals (subscribers) to the network, with multiple access of transmission routes.
- Transit Network: is a network connecting local networks of PSTN to each other (Public Network)
Exchanges of the transit network are organized to a multilevel network. Levels have several names, such as primary/secondary/international, class3/2/1, primary/sectional/regional.
- Tandem exchange: An exchange serving for handling congestions in the network. If the direct trunk between the two terminals becomes engaged then traffic will be transmitted through the tandem exchange.
- Private Network: A network connecting PABXs with each other.
Bibliography: Chapter 14 of [7]

