

Digital line section is similarly a block of the broadcast network, as the exchange, or the multiplexer, but this block is a bit long, its ends are many kilometres from each other. Digital line section has several special models:
Main elements of the digital line section:
A K átviteli közegen egyidejű kétirányú (full-duplex) jelátvitelt kell megvalósítani.
Ez nagy távolságok esetén irányonként külön átviteli közegen (négyhuzalos átvitel) történik.
Kisebb távolságok esetén megvalósítható a két irány jelének
egyidejű továbbítása egy átviteli közegen (kéthuzalos átvitel).
A vonalszakasz csatlakozási pontjai a hírközlő hierarchia szabványos
interfészei (G.703). Az LT vonali végberendezések feladata a szabványos
interfészek jeleinek illesztése az átviteli közeghez.
Az illesztés az
LT adóegységében a következőket jelenti:
We have to realize a full-duplex signal transmission on the K transmission medium. In case of large distances it can be made on separated transmission media by directions (four-wired transmission). In case of smaller distances there can be made the forwarding to the signals of the two directions at the same time and on the same transmission medium (two-wired transmission).
Connection points of the line section are the standard interfaces of the telecommunication hierarchy (G.703). Task of the line terminals (LT) is to fit signals of standard interfaces to the transmission medium.
Fitting in the transmission unit of the LT means the following:
Fitting in the receiving unit of the LT means the realization of the following tasks:
Built-up of the line terminals largely depends on the type of the transmission medium.
Regenerative repeaters bring the signal exposed to linear distortions and disorders back to its original shape section by section, and forward it to the next line section. A regenerative repeater is a connection of a line terminal receiver unit and transmission unit into a cascade to both directions. Regeneration inhibits the accumulation of distortions and noises along the line, but bit errors and jitters arise during the regeneration. Control system of the line section provides the regenerators with feeding energy, allowing the remote error determination of the impaired regenerators, or perhaps their switch to a standby.
Next figure shows the block diagram of one direction of a copper cabled baseband repetition section:
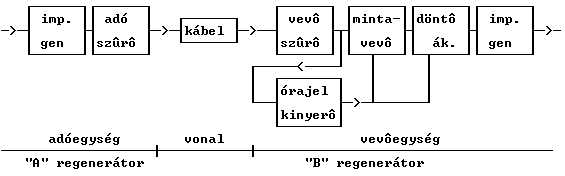
From the input of the transmitting filter to the output of the receiving filter the line section is an analogue channel, and for the good quality digital signal reception ? among others ? the criterion of the distortionless transmission (constant amplitude, and group delay characteristic in the operational frequency range) must be fulfilled, too. Main task of the transmitting filter is to limit the band of the transmittable signal to the operational frequency band.
The main task of the receiving filter (equalizer) is to provide the correction and equalization of the linear distortion of the copper cable and to provide the criterion of the distortionless transmission. The equalizer could be a fix in case of constant (established, rented) connections. At switched connections, e.g. in case of data transmission via telephone line, where the transmission characteristic of the line could be changed call by call, the transmission characteristic of the equalizer must be changed, too. For this task the transversal filter, which is a digital filter free from feedback is excellently appropriate.
Literature: Lajkó-Lajtha: PCM a távközlésben (PCM in telecommunication), pp. 346-387 (in Hungarian only)
Instead of LTs and regenerative repeaters nowadays the broadband modems are very preferred. The following figure shows the simplified block diagram of the optical line section:

The optical transmitter contains the device emitting the optical performance, and the electronic circuits serving for its operation.
The glass fibre conductor is a device, that allows the light to be forwarded.
The optical receiver contains the device transforming the optical performance into an electronic signal, and the electronic circuits serving for its operation.