Content:
Block diagram
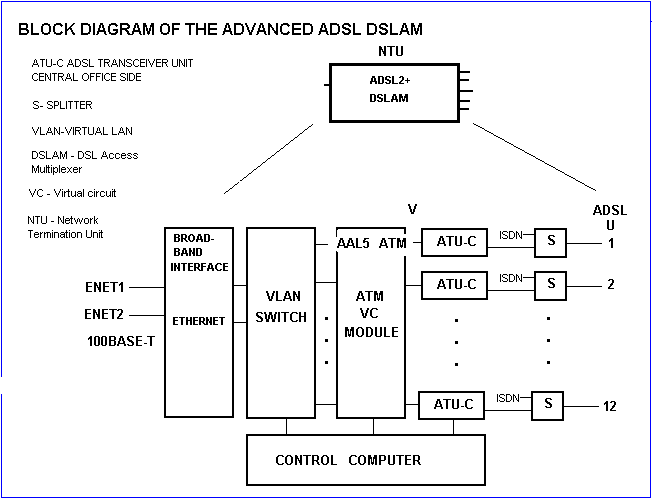
Parts of the device:
- Broadband Interface - broadband adapter of the ADSL system (2 pieces of 100BASET Ethernet).
- VLAN switch - It switches packet towards users according to the VLAN ID route identifiers located in the headers of Ethernet packets.
- ATM VC module - Ethernet packets are forwarded in ATM AAL5 frames towards modems. Application of the ATM provides compatibility with the earlier ADSL systems. Besides, it allows the generation of more virtual channels between the user and the provider.
- ATU-C - ADSL, ADSL2, ADSL2+ - Transceiver Unit Central office Side - Subscriber unit
which provides the connection between DSLAM and the user's equipment.
There are two types of ADSL subscriber units in DSLAM:
- ATU-C 12 POTS - 12-port transceiver, POTS works under ADSL (DSLAM type: AAM1212-51)
- ATU-C 12 ISDN - 12-port transceiver, ISDN works under ADSL (DSLAM type: AAM1212-53)
Main technical parameters
| Identification | Sign | Values
|
|---|
| Number of ADSL ports | 1 .. 12 | 12
|
| Number of 100BASET ports | ENET1, ENET2 | 2
|
Cable distribution box (MDF)
There are six ISDN and six POTS ADSL ports led out to the distribution box.
Splitter is built up to the DSLAM.
| connection box port | ISDN-ADSL port/
TELCON port | ISDN - U port/
TELCON port
|
|---|
| | a-b-c | d-e | circuit id
|
| 1 | 1 / P12 | 1 / P25
|
| 2 | 2 / P11 | 2 / P24
|
| 3 | 3 / P10 | 3 / P23
|
| 4 | 4 / P9 | 4 / P22
|
| 5 | 5 / P8 | 5 / P21
|
| 6 | 6 / P7 | 6 / P20
|
| CAa1 | 7 / P6 | - / P19 | IAL7
|
| CAa2 | 8 / P5 | - / P18 | IAL8 sim: LS-10.03
|
| | POTS-ADSL port/
TELCON port | POTS - tel port/
TELCON port
|
|---|
| 7 | 1 / P12 | 1 / P25
|
| 8 | 2 / P11 | 2 / P24
|
| 9 | 3 / P10 | 3 / P23
|
| 10 | 4 / P9 | 4 / P22
|
| 11 | 5 / P8 | 5 / P21
|
| 12 | 6 / P7 | 6 / P20
|
| CAa3 | 7 / P6 | - / P19 | PAL7
|
| CAa4 | 8 / P5 | - / P18 | PAL8 sim: LS-10.03
|
Management surface
DSLAM has a WEB management surface. We can find the web address, name and password in the black folder of the measurement.
In case of the laboratory no. 212 we should start the WEB browser from the PC connected to the 7. button of the console switch!!
Main menu
Basic Setting - (VLAN switch, interfaces (Ethernet, ADSL))
- System Information - identification data of the DSLAM (serial number, MAC address) can be read here.
- General Setup - we can configure here general device information (host name, etc.)
- User Account - administration data (username, password) can be programmed here.
- Switch Setup - DSLAM VLAN switch configuration
- IP Setup - DSLAM IP address configuration
- Enet port setup - DSLAM Ethernet interface configuration
- xDSL Port Setup - configuration of the ADSL U (line) interface and the ATM VCs (virtual channels)
- xDSL Profile Setup - configuration of the profiles of the ADSL U (line) interface and the ATM VCs (virtual channels)
- xDSL Line Data - measurement data of the ADSL U (line) interface
- VLAN - Virtual Local Area Network
- IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol
- Static Multicast
- Multicast VLAN
- Filtering - Packet filters on DSL ports
- MAC Filter
- Spanning Tree Protocol - (STP) link layer network protocol - IEEE Std 802.1D
- Port Authentication - connect to a Radius server
- Port Security - limiting the number of MAC addresses can be learnt on a port
- DHCP Relay
- DHCP Snoop - Allow traffic only on the addresses ditributed by DHCP server
- 2684 (former 1483) Routed Mode - ATM data flow multiplexing
- PPPoA to PPPoE - PPPoA -> PPPoE frame conversion
- DSCP - Diffserv Code Point
- TLS PVC - Transparent LAN service
- ACL - Access Control Logic
- Downstream Broadcast
- Syslog - System log server IP address
- Access control - SNMP, remote access services
Switch Setup - DSLAM VLAN switch configuration
Protocol layer:(Ethernet)
VLAN switch in the DSLAM has 12 ADSL (Port 1..12) and two Ethernet (ENET1, ENET2) ports. Switch makes the direction of Ethernet packets according to MAC addresses, and direction of tagged Ethernet packets according to VLAN_IDs. Switch can make a packet order rearrangement on the basis of the VLAN priority parameter. Switch can be automatically configured with the help of two protocols in the VLAN. They are the following:
- GARP (Generic Attribute Registration Protocol)
- GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol - Automatically Register VLAN membership across switches
Configuration of the VLAN-switch happens in two steps:
- 1. Configuration of the operation mode and the general parameters of the switch.
(These parameters are set according to the measurement exercise, their programming is not necessary.)
- 2. Programming of the static VLAN connections amongst the ports of the switch.
(We can do it in Advanced Applications/VLAN menu, according to the given configuration task.
Switch operation mode and its general parameters are the following:
- MAC Address Learning Aging Time - [10 ... 10.000 sec] ? Duration of a MAC address learnt by the switch in the address table. In case of programming 0 sec the switch will not forget the MAC addresses. (Coupling of MAC addresses and ports can be seen in the Management/MAC table menu.
- GARP timer timing values of GARP (IEEE 802.1.d)
- Join timer [100...65535 ms]
- Leave timer
- Leave All timer
- Port isolation active - on/off - it block the traffic among the ADSL ports, when it is switched on.
- MAC anti spooling - alarm generating, when a duplicated MAC address occurs
- Switch mode - standalone / daisychain - access mode of the uplink ports of two DSLAMs
- Priority Outgoing Queue Assignment
- Arranging Ethernet packets into the output queue on the basis of the VLAN User Priority parameter of entering packet -
priority levels: 8; enet queues: 4; adsl queues outgoing : 8
- Priority Level - [7..0] based on IEEE 802.1d
- 7 - network control traffic
- 6 - voice traffic
- 5 - video traffic
- 4 - latency sensitive traffic
- 3 - "excellent effort" traffic
- 2 - "spare bandwidth"
- 1 - "background traffic"
- 1 - "best effort traffic"
IP Setup - configuration of IP address of a broadband and managing interface
(These parameters are set according to the measurement exercise, their programming is not necessary.)
Default:
- IP [192.168.168.24]
- IP mask [255.255.255.0]
- Default Gateway [192.168.1.254]
Enet port setup - configuration of a broadband and managing interface
(These parameters are set according to the measurement exercise, their programming is not necessary.)
- Port ENET1/ENET2
- Active (on/off)
- Name ENET1/ENET2
- Speed mode (auto, 100 copper, 10 copper)
- Duplex (Full duplex)
Basic Setting - xDSL Port Setup - configuration of the ADSL U (line) interface and the ATM VCs (virtual channels)
Protocol layer:(ADSL)
In this menu we can configure ports of DSLAM ADSL and the ATM virtual channels assigned to the ADSL ports. In the ADSL modem WAN setup menu connecting to the port can the other port of the ADSL connection be programmed, and to give there the data consistent with the ones located here.
Configuration of multitudinous ports with the similar characteristics in many cases we can make easier with usage of configuration profiles.
Parameters of ports with the same characteristics with the same value we can edit once separatedly (profile), and we write only the identifier of the profile to the database of the port.
In the opening menu of xDSL Port Setup we can choose, which ADSL port we wish to edit. After choosing the ADSL port sets can be edited in several submenus (xDSL Port Setup, VC Setup, PPVC Setup). Besides, we have a possibility to a database manipulation in the opening menu (copy-paste functions).
Note: Provider products also SHDSL modems in this system, that is from the name xDSL derives.
Submenus of the xDSL Port Setup:
xDSL port setup (after selection of a port)
- #port (1 to 12) - number of the DSL port, which we can configure.
- active (yes/no) - switching the port on/off
- Port profile - identifier of ADSL port profile.
Here we can choose from existing profiles. Contents of the profiles can be seen in
the Port profile setup menu, and we can edit here new
profiles, if it is necessary.
- Mode - type of the ADSL frame ( auto, adsl2, adsl2+, gdmt, etsi )
- Alarm Profile - identifier of ADSL port alarm profile.
- IGMP Filter Profile - identifier of IGMP filter profile.
- ADSL2/2+ feature - Switching on/off ADSL2 ADSL2+ extra services and setting of parameters belonging to them.
- Annex L - Reach Extended ADSL2 - modems with
an extended range - (enable/disable)
(Annex L is one of the annexes of ITU-T Recommendation G.992.3 which describes service)
- Annex M - Double upstream mode (enable/disable) - extended channel capacity in upstream direction
- Annex I - All digital mode (enable/disable)
- The whole frequency domain is used for the ADSL transmission, there is neither POTS, nor ISDN service
- PMM - Power ManageMent (enable/disable) - Optimization of transmission performance in order to reduce the crosstalk noises.
- SRA - Seamless Rate Adaptation - Configuration without any service break in case of changing rate of the resource
- US INP - Protecion against impulse noise (Upstream)
- DS INP - Protecion against impulse noise (Downstream)
- MAX US TX PSD [dBm/Hz] - Maximum transmit power (Upstream)
- MAX DS TX PSD [dBm/Hz] - Maximum transmit power (Downstream)
- Power management parameters.
- L0 Time [s] - Minimal duration of the L0 state
- L2 Time [s] - Duration of the L2 state between two steps
- L2 ATPR [dB] - Aggregate Transmit Power Reduction - size of a level step
- L2 ATPRT [dB] - Aggregate Transmit Power Reduction Total - maximum allowed level reduction
- Max L2 Rate [kbit/s] - Maximum signal transmission rate belonging to the L2 state
- Min L2 Rate [kbit/s] - Minimum signal transmission rate belonging to the L2 state
- L0 to L2 Rate [kbit/s] - Rate threshold belonging to the L0 -> L2 state changing
- carrier mask (0...255(511)) - We have here a possibility to mask the bearer frequencies.
- US carrier (0..31)
- DS carrier0 (32..255)
- DS carrier1 (256..511)
VC ( Virtual Channels or Permanent Virtual Circuits or PVCs ) setup
Protocol layer:(ATM)
We can order eight VCs to every DSL port. We can use VCs for different services, or for realization of levels of a service. For the realization we can order PVIDs to VCs, and IEEE 802.1p priority parameters to them. These data can be ordered automatically to every received untagged frame.
- #port (1 to 12) - number of the DSL port, to which we order the VC.
We can order maximum eight VCs to every DSL port. (It is the basis of VC multiplexing.)
- Super channel (on/off) - If it is switched on, we can order only one VC to the ADSL port. VLAN_ID and User priority parameters are not used.
- VPI/VCI [0...255]/[32...65535] - path identifiers of the VC
They should be agreed with data set in the modem.
- DS VC profile - identifier of downstream VC profile.
We can select here from existing profiles. Contents of the profiles can be seen
in VC profile setup menu, and we can edit here new profiles,
if it is necessary.
- US VC profile - identifier of upstream VC profile
- PVID (Port VLAN ID) (1..4094) - VLAN-ID ordered to the VC.
(In case of Super channel it is 0.)
- Priority - 802.1p priority parameter ordered to PVID (User priority)
(In case of Super channel it is 0.)
PPVC (Priority based Permanent Virtual Circuit) setup
Protocol layer:(ATM)
PPVC (Priority-based permanent VC) service gives a possibility to order different
priorities to PVCs ordered to the same VLAN. PVCs can use 8 priority queues (levels) in
DSLAM.
In case of super channel this service cannot be used.
Entering to the menu, the upper part of the window serves for giving of the parameters
of PPVCs, and the lower part of the window we can see the list of the realized PPVCs.
Editable parameters:
- #port (1 to 12) - number of the DSL port, to which we order the PPVC.
- Encap - /vc/llc/ - Method of multiplexing into ATM AAL5 frame
- VPI/VCI [0...255]/[32...65535] - path identifiers of VC
- PVID (Port VLAN ID) (1..4094) - VLAN-ID ordered to VC.
- Priority - 802.1p priority parameter ordered to PVID (User priority).
We can edit elements of PPVC in the list of realized PPVCs, clicking to one of the elements of Members column:
- VPI/VCI [0...255]/[32...65535] - path identifiers of VC
- DS VC profile - identifier of downstream VC profile.
We can select here from existing profiles. Contents of the profiles can be seen
in VC profile setup menu, and we can edit here new profiles,
if it is necessary.
- US VC profile - identifier of upstream VC profile
- VC profile (ds us)
- Level - priority level
In this menu we can edit profiles used for configuration of ADSL ports.
In the opening menu of xDSL Port Setup we can choose, which ADSL port we wish to edit. After choosing the ADSL port sets can be edited in several submenus (xDSL Port Setup, VC Setup, PPVC Setup).
Entering to the menu, the upper part of the window serves for giving of the parameters
of profile, and the lower part of the window we can see the list of the realized profiles.
Editable parameters:
- Port profile setup ADSL line layer parameters
- Name - identifier of the profile
- Latency mode (fast/interleave) - path selection in the ADSL channel layer.
- Max. Rate [64...32000 kbit/s] - maximum rate to be provided (net data rate)
- Min. Rate [64...32000 kbit/s] - minimum rate to be provided (net data rate)
- Interleave Delay [1..255ms] - latency in the interleaved ADSL channel
- Max. SNR [0..31 dB default: 31 dB]
- Min. SNR [0..31 dB default: 0 dB]
- Target SNR [0..31 dB default: 6 dB]
- Up Shift SNR [0..31 dB default: 9 dB] - with this SNR growth system increases it rate
- Down Shift SNR [0..31 dB default: 3 dB] - with this SNR reduction system decreases it rate
- VC profile setup
Protocol layer:(ATM)
In this menu we can edit profiles used for configuration of ATM VCs.
Entering to the menu, the upper part of the window serves for giving of the parameters
of profile, and the lower part of the window we can see the list of the realized profiles.
Editable parameters:
- Name - identifier of the profile
- Encap /vc/llc/ - Method of multiplexing into ATM AAL5 frame
- AAL /aal5/ - Type of ATM AAL frame
- Class /cbr/vbr/ubr/ - traffic service category
- PCR [150..300000 cell/sec] - Peak Cell Rate
- CDVT [0..255] - Cell Delay Variation Tolerance
- SCR [150..300000 cell/sec] - Sustainable Cell Rate
- BT [0..255] - Burst Tolerance
- Alarm profile setup
In the alarm profile we can specify the threshold values of alarms (LOS, LOF etc.)
namely the number of the errors occurring during the time unit, which can already be
result an alarm.
- IGMP filter profile setup
In this profile we can limit the number of multicast channels in an IGMP group.
Parameters can be seen in this menu are measuring results of ADSL modems relating to ADSLlayer:
- Down/Up Stream Rate (kbps)
- Down/Up Stream Noise Margin (kbps)
- Down/Up Stream Attenuation (dB)
- Down/Up Stream Attainable Rate (kbps)
- Service Mode
- Trellis Encoding
- Down Stream Interleave delay
- Up Stream Interleave delay
- Down Stream Output power
- Up Stream Output power
- ATU-R, ATU-C vendor id, version number, serial number
VLAN - Virtual Local Area Network
With the help of this function we can divide a physical LAN to several virtual LANs. It is a possibility to separate users, which can happen practically on the ports of VLAN switch.
- VLAN status - in this table we enumerate the configured VLANs and their main parameters.
- Static VLAN Setting - We can configure a VLAN in this menu
- VID - = VLAN ID is the identifier of a VLAN in the configuration at the same time
- Active (yes/no) - switching VLAN on/off
- Name - identifier (name) of the VLAN
- VLAN ID (1..4094) - VLAN identifier in the DLC MAC frame
0 value cannot be programmed (it is the identifier of the untagged or priority frames).
- We can assign switch ports of the VLAN to the VLAN in the further parts of the menu.
- Port - identifier of DSLAM port ( ENET1, ENET2, 1 ... 12 )
- Control (fixed / forbidden) - port is/is not member of the VLAN
- Tx Tagging - can the port send the VLAN ID by transmission /or cannot (Tagged/Untagged T/U)
- VLAN Port Setting - We can program here the handling of Ethernet frames arriving to the ports of DSLAM:
- Port - identifier of the DSLAM port ( ENET1, ENET2, 1 ... 12 )
- PVID (Port VLAN ID) (1..4094) - we assign this PVID to the untagged frame received at the given port .
- Priority (0..7) - we assign this priority to the untagged frame received at the given port.
- GVRP - permission of the usage of an automatic VLAN registration protocol (only on ENET1, ENET2 ports).
- Acceptable frame type - (All / Tagged only) Programming of the frame type received by the port

