Reference models - General build-up of SPC/VOIP (TDM/IP) exchanges, communication managers (CMs)
Implementation: DEFINITY exchange, BCM 50 exchange
The so called communication managers (CMs), that are electronic exchanges controlled by a stored program (SPC/VOIP (TDM/IP) in the nodes of the line switched broadcasting networks with integrated services (ISDN) (see chapters 14.3 .. 14.5 in [7]).
Explanation of the name:
- elektronic: exchange is fully made of electronic circuits.
- digital: connecting lines to each other is made either by a digital switching field operating on the principle of time division (TDM (PCM)) - switching field (SPC), or Packet (IP/RTP) switch (CM). It means, that news to be switched must be forwarded in format of a digital signal towards the exchange. News arriving in an analogue format, first must be digitalized in the exchange.
- stored program controlled (SPC): control of the switching field is made by a built-in computer,on the basis of the program stored in the memory of the computer. Control with a stored program realizes numerous flexible services, that can be programmed by the user (call holding, call redirection, automatic recalling).
Main units of the exchange:
- Switch - Switching field of the classic digital exchange operates on the basis of an attached time division principle. Its essence, that we can digitalize the signal of lines to be connected, and arrange into PCM frames Switching field operates after that, that it replaces the content of time-gaps of calling and called lines (trunks).Beyond news to be switched, exchange must also handle signalling messagesof the lines. Signal is a data replacement serving for build-up and control of line-switched connections. Switching field switches digitalized signals towards the computer of the exchange in format of messages.
Switching field of a modern digital exchange operates on the principle of packet-switching. Its essence, that we arrange signals of lines to be connected with each other to the so called RTP packets after digitalization. Switching field operates after this, that it directs packets arriving from the calling line towards the called lines.
- Computer - Computer is build up unversally (CPU, RAM, background storage). Besides, it contains some special peripheries (signal message adapter, acoustic signal interface for reception and transmission of sound frequency coded signals (e.g.. DTMF dial sound), too. Database describing the giving exchange configuration is located in the memory of the computer besides the operating program - so have many devices are attached to the exchange, and what kind of services did we assign to them? Content of the database can be modified by the operator of the exchange with data administrative programs, it is the basis of the user level programming of the exchange.
- Peripheral units - Its tasks is to adapt device lines and trunk lines of the exchange (periphery) to the switching field, and telephones, terminals, partner exchanges attached to them. Adaptation can be realized through various standardized interfaces.
- Cross connect - Attachment of many lines happens physically at the cross-connect of the exchange. Cross-connect is a large connector line, and terminals of peripheral units of the exchange are connected to one of its sides, and lines arriving from the devices are connected to the other side. There will happen the connection of these terminal to each other.
The following figure demonstrates connection of peripheries and a SPC/VoIP exchange/CM:
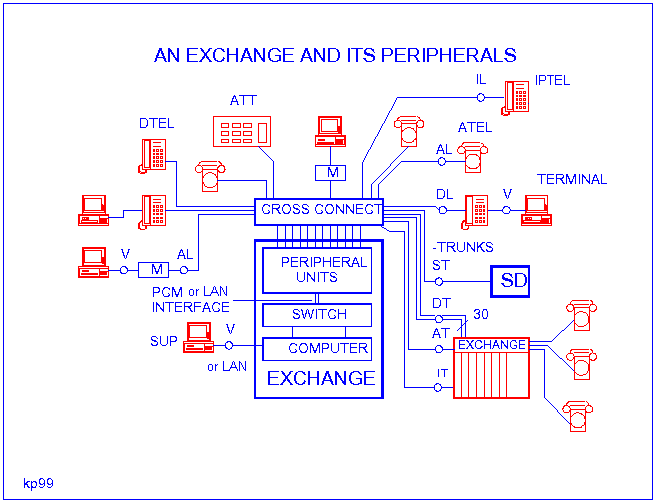
Devices attachable to the exchange:
- ATEL - Common, analogue telecommunication devices which connect to the exchange through the analogue device lines marked with AL.
- DTEL - Digital (ISDN) telecommunication devices which connect to the exchange through the digital device lines (ISDN U interface) marked with DL.
- IPTEL - IP telephones which connect to the exchange through the Ethernet interfaces marked with IL.
- EXCHANGE - There are another exchange(s) attachable to the exchange, generating a network. Connection of the exchanges happens through the so called trunk lines.
Trunk lines can be realized - similarly to the device lines - by several telecommunication technologies: AT - analogue trunk, DT - digital (PCM, ISDN) trunk, IT - VoIP trunk.
- ATT - Handling set. It is a special telecommunication device, which is operated by the operator of the exchange (an auntie/uncle at the calling exchange). In absence of selection external calls arriving to the exchange are arriving here, and the operator connects the called line.
- SD - There are tools attachable to the exchange, which can provide a special service (radio pager, dictaphone, answering machine, voice mail, etc.). Their connection is provided by the ST - special trunk.
- SUP - it is the so called administrative (supervisor) terminal. Operator can program the exchange through this.
Connecting to each other the exchange and devices attached to it will happen at standard connection surfaces, e.g. the interfaces marked in the following figure:

