- Internet protocol
- IP address - an IP address used in AxD generally. These IP addresses categorized as follows:
- Interface (IP) address - This address refers to the IP interface.
- Application (IP) address - An IP address assigned to an application
- Interface-related IP address - An IP address assigned to an application when the application itself has been assigned to an IP interface, too.
- Type
- Media Gateway - (application) identifies the virtual (local) MG in the AXD.
- Internal - reserved and restricted IP addr. (0.x.x.x, 10.0.0.x, 10.30.x.x)
- SCTP - SCTP interface address
- CS/NB - Circuit Switched/Narrowband address (interface-related)
- OAM - HTTP/FTP/NTP
- Interface - IP address assigned to a physical interface
- Router ID - is a loopback interface address that can be used to access the node without specifying an interface IP address. The Router ID must be configured before any IP interface can be created. The Router ID is used as the BGP identifier. The Router ID can be any non-reserved and non-prohibited IP address. After specifying this a loopback route will be also created in the node.
- Mask
- Interface identifier
- User-provided name
- IP interface - An interface which closes the IP layer. (It can be realized for Packed base LIB and SP.)
IP net to media table (ARP) - IP address-MAC address conversion
Attributes:- Type (semidynamic, static)
- IP address
- MAC address
- Poll interval peer up/peer down
- Event filter
AMS menu: Switch Fabrik/Link
IP interface menu:
Attributes:- IP interface identifier -> Index
- Physical interface identifier -> Port
- Interface address/mask
- Synchronization flow
- State (admin/op)
- Type (IP/Ethernet, IP/POS)
AMS menu: IP services/Interfaces
- IP termination
Attributes:
- MG Id.
- IP termination Id. -> Port
- Packetization time
- Rem interface rel IP addr
- Remote (UDP) Port
- Loc interface rel IP addr
- Local (UDP) Port
AMS menu: MG IP termination
- Layer - réteg - Notation used for the internal function disposition in the case of composite interfaces.
Examples for standardized layer structure: the (OSI model) of the Packet Base interface, the SDH/STM-1 interface, or the ATM interface - Line Interface
- LI - external, user side, line interfaces of MSS ET, terminations of the external links
+--------+ +-----+ ---| - ET - |--| |-- +LI----SP+ | | | | | | | SC | - LIB - Line Interce Board; the circuits of interfaces are located on these boards.
Circuits of MSS LIB-ek realize the standardized interfaces of the following telecommunication technologies:
Interface notation Technology EM Type Description/Functions optical interface 1000BASE-SX/100BASE-TX
Gigabit Ethernet (GBE)/Fast Ethernet (FE)Packet based GBE/FE Ethernet 1x1000BASE-SX + 1x100BASE-TX or
For VoIP applications.
PT board joins it to SC.
Functions:- GBIC - Optical transmitter/receiver, 802.3 line interface
- Line Tx/Rx - line transmitter/receiver
- MAC framer/deframer, Layer1 overhead handling (preamble, FCS)
- Management, attributes (AMS)
- Supplementary services
- Fault detection (Link alarm) (BFD, Remote fault)
- Auto-negotiation
- Flow control
- Link statistics
- IP interface
POS ATM ET 155 4xSONET/STM-1 / OC3 ATM (POS)
For VoATM applications
(we do not teach this topic)MM, S1.1, L1.1, L1.2 E1 interface CE (TDM, PCM, PDH ) ET2 CE 32 CT
(E1 DS1 J1)2 Mbit/s Exchange Terminal (ET2),
32xE1 interface For Circuit Emulation (CE) and Voice applications
CT board joins it to the SC.
Functions:- Line Tx/Rx - line transmitter/receiver
- Framer/Deframer - Assembling/diassembling E1 frame.
- Overhead Insertion/Extraction - The E1 time frame
- E1 - ATM AAL1 frame conversion (CT board)
- Management, attributes (AMS)
- Supplementary services
- Fault detection (Link alarm)
- Performance monitoring
- Link statistics
- Tone generation (CT board)
- Echo cancellation (CT board)
STM-1 interface CE (TDM, STM, SDH ) ET2x155-S1.1 CE CT 2x155Mbit/s Exchange Terminal (ET2x155, 2xSTM-1 interfaces),
2x63xE1 interfaces For Circuit Emulation (CE) applications,
multiplexed according to SDH VC-12 into STM-1 frame.
CT board joins it to the SC.
Functions:- Line Tx/Rx - line transmitter/receiver
- Framer/Deframer - Assembling/diassembling STM1 frame.
- Overhead Insertion/Extraction - THE STM-1 time frame
- Management, attributes (AMS)
- Supplementary services
- Tributary mapping (VC-12/E1)
- Fault detection (Link alarm)
- Link statistics
- Link Performance monitoring
- Testing
- Protection
S1.1 single mode Frame Relay Not implemented
Interface sublayers
The above mentioned line interfaces have many attributes. For perspicuityin AMS these attributes have been organized in multiple submenus (interface sublayers) according to the layered structure of interfaces and Type attribute has been used to indetify each of them. Following table shows the existing submenus:Interface sublayer, Type Id. Interface sublayer name Leírás ATM ATM interface CES Circuit Emulation interface Ethernet IP mod PDH PDH2 interface E1 Line interface attributes PDH E1 interface STM-1/E1 Line interface attributes PPP SDH (RS, MS) STM-1 line interface SDH PATH (HP - Higher order Path) VC-4 interface SDH LOW PATH (LP - Lower order Path) VC-12 interface E1 Line interface attributes: (PDH2 sublayer)
- Type - PDH
- Nominal speed 2048000 bit/s
- Loopback type off, line, local
- Tx Clock source - Netsync -source: the PHLC, Looped -source: clock signal recovered from the signal received on Rx interface.
- Line type - unframed, framed, framed CRC4
- Line coding - HDB3, AMI
- Circuit Id.
- AIS alarm activation on, off
- RDI alarm activation on, off
The attributes of STM-1 interface can be edited in submenus fitted to the SDH layer structure:
- AMS->SDH interface sublayer - Transmission media layer (STM-1 line interface (RS, MS)) attributes:
- Type - SDH
- Name - s011802
- Link rate - 155 520 000 bit/s
- Loopback type - off, line, local
- Tx Clock source - Netsync -source: the PHLC, Looped -source: clock signal recovered from the signal received on Rx interface.
- Framing type - SONET, SDH
- Line coding - NRZ, CMI
- MS-AIS alarm activation - on, off
- MS-RDI alarm activation - ON/OFF
- MS-RDI insertion activation - AutoInsertion, off
- REI insertion activation - AutoInsertion, off
- Higher order Path (HP) layer attributes (AMS->SDH path sublayer):
- Type - SDH PATH
- Name - h011802
- ATM transfer capability - 149 760 000 bit/s
- AU-AIS alarm activation - ON/OFF
- HP-RDI alarm activation - ON/OFF
- HP-PLM alarm activation - ON/OFF
- HP-TIM alarm activation - ON/OFF
- HP-RDI insertion activation - AutoInsertion
- Trace identifier sent, expected (hex), received (hex)
- Signal label received:
- Lower order Path (LP) layer attributes (AMS->VC-12 interface sublayer):
- Type - SDH LOW PATH
- Name - l010 301 001
- Nominal speed 2048000 bit/s
- TU-AIS alarm activation - ON/OFF
- LP-RDI alarm activation - ON/OFF
- LP-PLM alarm activation - ON/OFF
- Signal label received: Asynchronous
- AMS->E1 interface sublayer - Circuit layer attributes:
- Type - PDH
- Name - o010 301 001
- Nominal speed 2048000 bit/s
- Loopback type - off, line, local
- Line type - unframed, framed, framed CRC4
- Circuit Id.
- AIS alarm activation on, off
- RDI alarm activation on, off
The attributes of GBE interface (PHY, MAC, LLC, ARP, BFD) (Ethernet termination)
- Type - ETHERNET
- Name - e010502
- Operational state - UP
- Link rate [bits/s] - 1 000 000
- Link type - GBE SX (multimode), GBE LX (single or multimode), FE (Fast Ethernet)
- Media available state (available, not available, going off line, remote fault, auto-negotiation error, unknown)
- Auto-negiotation admin. state
- Remote fault advertised/received
- Flow control admin. state switch (disabled, Tx enabled, Rx enabled, Tx and Rx enabled) (GBE only)
- Flow control op. state indicator (disabled, Tx enabled, Rx enabled, Tx and Rx enabled) (GBE only)
- MAC address indicator (e.g.: 00:01:EC:FF:8F:EB) (OUI: 00:01:EC Ericsson)
- GBIC - GigaBit Interface Converter (vendor name, port number, revision, ser. number)
IP net to media table
- LI - external, user side, line interfaces of MSS ET, terminations of the external links
- Link
- transmission route, data link generally
Synonyms: channel - csatorna, circuit - áramkör - In MSS: duplex transmission route (data link) between two nodes
+--------+ +--------+ +-----+ | AXD x---- link---x | | | | - ET - x---- link---x - ET - | | | | x---- link---x |-i-| | +SP----LI+ +LI----SP+ | | | | | SC | +--------+ +--------+ | | | ext. x---- link---x - ET - |-i-| | | - ET - x---- link---x - ET - | | | | vendor x---- link---x - ET - | | | +--------+ +LI----SP+ +-----+ ET - exchange terminal LI - line interface SP - switch port interface SC - switch core link - external link i - internal link x - interfaceIdentifying attributes of a link :- Line interface location
- Name - a unique identifyer given by the user
- Id. - an integer
- Type - type of link/interface
- internal/external
- H.248 control link
Type:- Internal (ML-MGWIC) (Link Id. -> Localport)
- SAAL - ATM transport (Link Id. -> VPI)
- SCTP - IP transport (Link Id. -> Localport)
- IP interface
- LI interfaces - termination, interface of the link
- CE E1
- CE STM1 SDH path
- ATM
- Packet Base
- ATM interface index - the unique identifyer of the link in ATM interface sublayer.
- State
- Administrative state
- Operational state
- Provisional state
Miscellaneous services of the links:
- Fault detection (Link alarm)
- Link statistics
- ispect link error counters
- start supervision of the QoS
- Link performance monitoring
- determ. traffic load, inspect QoS
- Link testing
- Down state, Rest button push
- Return AMS event list: eqmLinkTestResultEvent
- Link protection
- Tributary mapping
AMS menu: Equipment/Configuration/Equipment Module/Link or Switch Fabric/Link
- transmission route, data link generally
- Link alarm - Maintenance signal of the link
The function of the maintenance signals is to indicate the operable/failes state of the link and to provide indication to user for troubleshooting in the case of failure. The sources of the maintenance signals of a link are measurement results of (hardware and/or firmware) diagnostic tools of the interfaces of the link. The maintenance signals of diverse interfaces can be tracked back to some basic types. The maintenance signals are the harsh area of the standardizing, notations are not clear and mostly manufacturer specific. Following table tries to straighten this situation.Label Definition Interface Description AIS Alarm Indication Signal E1, STM1 LCD Loss of Cell Delineation ATM LMF, LOM Loss of Multiframe E1 LOF Loss of Frame - no frame synch E1, STM1 LOP Loss of Pointer STM1 LOS Loss of Signal - no signal E1, STM1 E1, STM-1 PLM Payload Label Mismatch STM1 RDI Remote Defect Indication (former FERF, RAI) E1, STM1, ATM RDI, ATM: RDI REI Remote Error Indication (former FEBE) E1 TIM Trace Identifier Mismatch STM1 Alarm signals used previously:
Label Definition Interface Description FERF Far End Receive Failure STM1 RDI FEBE Far End Block Error E1 REI RAI Remote Alarm Indication E1 RDI alarm activation on, off - Switching on/off the displaying of the received alarm messages on the interface in AMS.
alarm insertion activation autoinsertion, off - Activation of the answering the received alarm messages with alarm sending.
RDI - Remote Defect Indication - Receiving of a remote alarm on the local port of the link which caused by the reception failure of the remote prot (i.e. the transmission failure of the local port). This is the most common alarm answer.
link +-------+ error +-------+ | local |--->--- x --->----| remote| | port |--------<---------| port | +-------+ RDI +-------+Answer alarm messages:Label Definition Interface Received alarms RDI Remote Defect Indication STM1 LOS, LOF, MS-AIS AMS Menu: Event&Alarm->Current_Alarm_List
Clicking on the relating line the detailed alarm signal can be read. - LMT - Local management terminal.
- Location - identify the (physical) location - Circuit, Port, IP interface, Room ,
- Loopback address see Application IP address
- LOVC - Lower Order Virtual Container - STM-1
- LP - Lower order Path - STM-1
- Mask (subnet mask) -> interface address
- MGC - Media Gateway Controller - H.248 term
- Controls the parts of the call state that pertain to Connection Control for media channels in a MG.
- a part of the control of MSSNsof EIN/TSS VoIP
- Media Gateway (MG, MGW) - H.248 term
MG converts and switches media between the networks of different telecommunication technologies.
Typical apllication: adaptation of circuit switched (TDM) networks to packet switched (IP) networks. (TDM/IP conversion)
MG is a part of an MSS application. There may be more MG inside an MSS and MSSN, they are controlled the Media Gateway Controller (MGC). Example MSSN of TSS has been build up also from MGs.
MG is physically a subset of AxD's EMs,+-----+ +--------+ +-----+ +--------+ |PABX |---- TDM ---| - ET - |--| SC |--| - ET - |---IP--- +-----+ +LI----SP+ | | +SP----LI+ +-----+ +----+ | CP | +----+actually it contains the SC and the SC side interface circuits of ETs. when we configure them the elements of this subset have been called Device in the AxD terminilogy . MGs can be programmed in the Voice menu.
Main functions of the MG:- Realization of Point-to-point connections (semipermanent and dynamic)
- media conversion
- event detection, signal insertion
- connection management
- spc
- dyn conn
- MG connected to an IP network that passes signalling messages to the MGC.
- Supplementary services
- ec
- law conversion
- tonegen
- DTMF detection
- Name - identifier of MG (here: b211, b212, b213)
- IP address
- IP Epheremal Termination name
- IP parameters
- GCP parameters
- Devices
- Control links
- Tone type
- CS_NB (interface related) IP address and UDP Port range
AMS menu: Voice/Media Gateway
- MG, MGW - Media Gateway - H.248 term
- MIB - Management Information Base
An abstract description of a network element from the management systems point of view - ML - Mediation Logic - Közvetítő logika
- MS - Multiplex Section - STM-1
- MSS - MultiService Switching - multifunkciós kapcsoló. (implementation: this is the Ericsson AxD 305).
- Introduction
- Hardware architecture
- the EM (Equipment Module)
- Services and applications of MSS
- a network element of the MSSN
- Configuration: via MT.
- Administrative identifiers: Next attributes have been used to identify the MSSs within the network:
- Number - Number of MSS in the configuration database of AXDs (here: 1,2,3).
- MSSN Id. - Node identifier of MSS (here: MSS-1, MSS-2, MSS-3)
The number in MSSN Id. is the same as the number of MSS in the database of AXD. - Room - The identifier of the room where the MSS locates. (here: B211, B212, B213)
- Name - The identifier of MSSs in the Media Gateway configuration database of AXDs (here: b211, b212, b213)
In the telecommunication test network this names are the same as the Name identifiers defined in Media Gateways and the Name prefixes of Media Gateways' Device components. - Config Id. - Manufacturer configuration identifier of MSSs (here: 036, 030, 037).
- MSSN - MultiService Switching Network (This is the network built up from MSSs (actually from AxDs)).
The manufacturer of the equipments constructed many types of networks from MSSs mainly for telecommunication applications (Voice & Telephony Services):- EIN - Engine Integral Network - VoIP network on ATM
- EIN - Engine Integral Network - VoIP network on IP
- EMM - Engine Multimedia Solution - Multimedia network on IP
- TAG - Telephone Access Gateway - PSTN network adaptation into IP network
- TSS - Telephony Softswitch Solution - test network for the implementation IP based switched telecommunicvation service
Topology:
The equipment (Network Element) located in a Node of MSSN may be an AXD equipment (MSS) or a switching equipment (Exchange) provided by an other manufacturer (in telecommunication test network of the department e.g. a Definity exchange). The duplex transmission pathes between nodes have been called links. Links have been terminated in ports of network elements.Identifiers:
- Node - Csomópont
- In the case of MSS this is an identifier set
- Exchange Id. - Identifier of a switching equipment provided by an other manufacturer (here: D1, D2, B3, H3).
- Link Id. - User identifier of a link (here: D1-D2, D1-B3, D2-H3, B3-H3)
- Port Id. - AxD Port address (e.g.: 1/3/1 (subrack/slot/port))
A VoIP (EIN/TSS) network has 3 main elements:
- The IP network which transmits voice, signaling (CS-NB), connection control messages (CC), and as well as OAM messages.
- Converters, switches between IP network and TDM network, Media Gateways (MGW) within MSS.
- Control of the network: the Telephony Server (TS).
The MSSN in the test network has been based on EIN/TSS, additionally Circuit Emulation (CE) application also has been used in the test network.
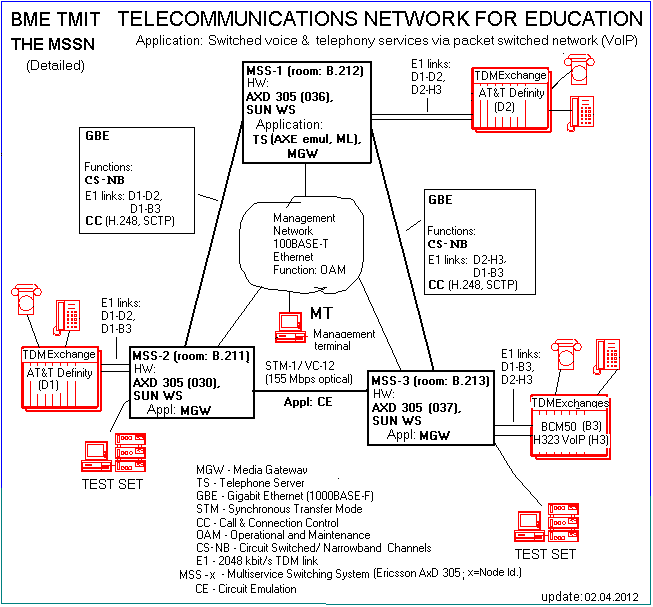
SUN workstations belonging to AxDs have many functions:
- AXE simulator
- Connecting AXDs to the management network
- Configuration of AXE simulator
- MT - Management terminal - Menedzselő Terminál - Access to the WEB user interface of MSSs (AXDs).
This WEB user interface has been called AMS (AXD Management System) in the AxD terminology.
The MT (actually a PC) may be connected directly to a LAN port of one of the CP board of the AxD (Local Management Terminal LMT) or via a management IP network (Remote Management), this latter one has been used in the laboratory. The user guide of the Az MT can be found in the Usage of the data administration and diagnostic programs chapter of the tutorial.Most important menus of WEB user interface have been listed below:
- Equipment/Configuration - Hardware configuration of ETs, SCs, CPs (i.e. the EMs)
- IP Services (IP network level services)
- Permanent Connections - Creation of CE PVCs in SC
- Switch Fabric - Configuration of SC (Switch Core) ATM switching network (Circuit Emulation, Link)
- Voice - Programming Voice & Telephony Services application.
Detailed description of the menus of the user interface and the manufacturer documents of the AxD are available only in the laboratory and only for teaching purposes. Copying these documents is strictly forbidden!
- MTU - Maximum Transmission Unit (IP protocol)
- MSOH - Multiplex Section overhead - STM-1
- Name - An MSS EM, Device attribute, unique identifier.
- Network element - Hálózati elem - see: MSSN
- Node - Network node - see: MSSN
- Number - An EM attribute.
- Packages - service (software) packeges
- V5.2 package: Handling of the signaling messages of ITU-T's Access Network (1..16 E1 links)
- H.248 packages: Chapter 12. - Package Definition; H.248.1 Annex E - Basic Packages
- Path
- Generally a set of transmission pathes (linksek), circuits, channels (trunk) having the same properties.
- path layer (SDH): transmission service for circuit layer.
- VP - Virtual Path (ATM) VPI - Virtual Path Identifier (ATM)
- PC - Permanent Circuit/Connection - Permanent (leased) circuit/connection
- - Permanent Connection (CE)
- - PVC - Permanent Virtual Circuit (ATM)
- PDH - Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy / interface, index
- PHLC - Physical Layer Clock - Internal clock signal source of the AXD. If AXD network use synchronization PHLC comes from the network.
- Physical Termination, Location, Interface Identifier
- PLM - Payload Label Mismatch - Link alarm
- Port
- An interface, a standardized connection point (circuit, port) of the MSS
- Termination of a link. The nearest one is the local while the farest one is the remote port.
- Port physical location identifier (AXD Port address, TDM Exchange)
It identifies the ciruits, circuit terminations, interfaces of the network element in the database of the AMS. - IP/UDP port identifier (IP interface / VoIP circuit)
- Port physical location identifier in AXD
The identifier contains the following attributes (Port address):- Subrack - Subrack identifier in a Rack (in a cabinet)
Subrack is a mechanically integrated frame froming a single unit into which the boards of the equipment can be plugged. A large scale equipment may consist many subracks which may be located in one or more rack.
(In the network of the TMIT an AxD have been located in single subrack so the identifier is always "1" here) - Slot - Identifier of the place for the board within a subrack
(In the network of the TMIT an AxD has 9 slots with identifiers: 1,2,3,4,5,6,18,19,20 numbering from the bottom). Two boards can be plugged into a slot (from front and rear side; this is described by the Side parameter in the database.)
(The meaning of the front and rear side is relative, because the boards which we found in front of us in the laboratory are mentioned as rear side boards in the documentation.) - Port - Identifier, number of the interfaces located on the board
Example: The port address (Subrack-Slot-Port): 1-6-3 in the AxD with Name: b213 identifies an E1 interface, because in the slot 6 there is an 32-port E1 interface board (EM type: ET2 32 CT). (As separator beside of "-" also the "/" character can be used.)
Synonimes of the port address in the different menus of AxD: Physical Location, Interface Identifier, Physical Interface Identifier . Also the port address completted with Subport and/or Service parameters have been called to Interface identifier in the AMS menus. Example: 1-3-1-1-u, or 1-6-1-u.
Moduls and cicuits of the AxD can be listed in the Equipment/Configuration menu according to EM - Equipment Module, Board, Slot attributes. - Subrack - Subrack identifier in a Rack (in a cabinet)
- The port physical location identifier of other telecommunication equipments (Definity, BCM50) contains similar attributes.
- IP interface
VoIP (CS_NB) circuit identifier
- IP address (relative) Local/Remote IP Epheremal
- UDP port Id. Local/Remote port, UDP Port Range Low
- POS - Packet over SONET/SDH - Transmission of IP packets over SDH network.
- Profile - funktional unit descriptor, it contains the mandatory and optional capabilities of the functional unit. The following funcional units have a profile:
MG, VP
- Protected domain
- PTB - Packet Termination Board
- PVC - Permanent Virtual Connection
- RDI - Remote Defect Indication - Link alarm
- REI - Remote Error Indication (former FEBE) - Link alarm
- Roles CP roles
- Room MSS location identifier
- Router ID - lásd IP address types
- Routing table - The routing table is a real-time database
in the AXD 301 node, which is used to store information about
routes in the network.
- RS - Regenerator Section - STM-1
- RSOH - Regenerator Section overhead - STM-1
- RTP - Real-time Transfer Protocol - Real-time transport protocol for forwarding voice and picture over IP network.
- RTP transcoding
- RTP over AAL5 - adaptation between AAL1 and RTP over AAL5
- RTP IWU (via VPB)
- RTP IWF
- Rx - Receive - vétel
- SC - Switch Core - An (ATM) switch to interconnect the ports of ETs.
+--------+ +-----+ +----+ --| - ET - |--| |--| CP | +LI----SP+ | | +----+ | | +--------+ | | --| ET |--| SC | +--------+ | |The SC operates with (duplicated) internal cells; its interface towards the outer world is the SP. - SCN - Switched Circuit Network - Circuit switched network realized on TDM basis.
- SCTP - Stream Control Transfer Protocol - is used to transport H.248 from the TSS MGW to the MGC. A transport layer protocoll simmilar to TCP.
- SDH - Synchronous Digital Hierarchy - It implementation in MSS: the STM-1 interface
- SDH interface sublayer (AMS)
- Section - szakasz, rész - A notation used for the internal function division in the case of complex interfaces, similar as the Layer.
Example the SDH/STM-1 interface
- Service - szolgálat
- SG - Service Guide - AxD documentation class
- Shared Risk Group (SRG) is a concept that maps a property assigned to an IP interface. The control is through an H.248 package used to ensure availability of mutually exclusive paths within an IP network to minimize the risk of total communication failure. See the H.248 standard documents for more details: Ref. [21] and Ref. [22].
- Signalling channel - In this document, a signaling channel
is a configured entity that is used for signaling, for example,
an H.248 signaling channel or an Operations and Maintenance (OAM) connection,
transporting data from an IP interface to one or both Control Processors (CPs) in a CP pair.
The signaling channel is configured to an IP interface and has a certain bandwidth and PSC associated with it.
The signaling channel is stored persistently in the database.
- Signalling Port - ATM Signalling port - The ATM signalling application is not implemented
- Slot - Port attribute
- SONET - Synchronous Optical Network - American standard for "SDH"
- SP(C) - Switch Port/(Circuit) (Termination Board) - SC side interface of MSS ET
+--------+ +-----+ ---| - ET - |--| |-- +LI----SP+ | | | | | | | SC |MSS SPs adapts the standardized interfaces of the following telecommunication technologies to the SC:Technology EM Type Function Packet based PT, PTB - packet forwarding, IP interface
- traffic management, firewall functions for IP & MPLS traffic
- AAL5 segmentation/reassembly
- converting RTP VoIP traffic from/to CE (AAL1, G.711 built in jitter buffer)
ATM AT, ATB - ATM cell switching
- scheduling, traffic management
- interworking with: ATM-line boards, CE-boards
CE (TDM, PCM, STM) CT, CTB - ATM cell switching
- ATB + tone generation & echo cancellation
- interworking with: CE-line boards
Panels of SPs are also called to Termination Board, referring to their main fuction, i.e. the termination of the connections.
AMS Menu: Equipment/Configuration - SOH - Section overhead - STM-1
- SPC - Semipermanent connection (VoIP, CE)
- States - Indicators and switches
- Administrative state (EM, Link attribute) - a switch, which enables/disables the related device.
Possible values:
- blocked, down - device is switched off, its attributes can be edited
- unblocked, up - device is switched on, its attributes can not be edited. The actual fact of the operation indicated by the Operational State.
- Soft blocking - Soft blocking is a state of an interface, similar to the Administrative state. When the Soft blocking state is Down, new connections cannot be established on the interface, but existing connections are kept.
- Operational state (EM, Link attribute) - indicator
Possible values:
- down - The Administrative state of the device is down: either the device
is out of order or there are no signal on the input interface of the device.
No signal in the case of E1 interface:- Nothing is connected to the interface
- There is signal on the input of the interface but it is AIS. This situation can also happen if we have looped back an interface with attribute Line Type=unframed on the line side.
- up - The Administrative state of the device is up, it is ready to transmit/receive traffic.
- dormant (sleeping) - This is the value of the Administrative state of the device, if the operational state of the LI, SP, EM belonging to the device is down; LI, SP is out of order; in the case of sublink the state of the underlaying sublayer (SDH LOW PATH) is down or dormant.
- testing - test function of the device is switched on
- down - The Administrative state of the device is down: either the device
is out of order or there are no signal on the input interface of the device.
- Provision state (Link) - availability indicator
Possible values:
- provisioned - the device is available
- unprovisioned - the device is not available
- Administrative state (EM, Link attribute) - a switch, which enables/disables the related device.
Possible values:
- STM-1 (Synchronous Transport Module, level 1) - 155 Mbit/s SDH interface,link
- Sublayer - (al)réteg
- An other name for layer, or the division of a layer.
- Interface sublayer - In AMS the grouping of interface attributes according sublayers.
- Sublink - in the case of multiplexed link the component links are the sublinks.
E.g. in the case of STM-1/VC-12 the sublinks are the connected E1, VC-12 lines.
id: 1(1.1.1) 4(1.2.1)
- Subport - a termination of the sublink
- Subrack - Port, EM attribute
- Switch Device Id. - MGW Device identifier of an AxD within the AxE exchange. The conversion table of the Switch Device ID. and the AxE Termination Id. have been stored by the ML.
- Termination - termination of a Connection in MSSN. - H.248 term.
A Termination is source/sink one or more media or control streams. Beside of the termination of payload an important task is the termination of the framing of the payload, too (IP termination). Termination can be:- physical
- - Packet, ATM, CE Terminations - i.e. the circuits of the PTB, ATB, CTB Termination Boards. These terminations are static.
The attributes of Termination:
- Termination Id: Device name + (PCM) channel (timeslot) number (1...31) Example: b211/1/3/1/1..31
- Termination Id (in ML Device menu): Switch Device Id. + (PCM) channel (timeslot) number (1...31)
- - a subset of the above mentioned circuits have formed the so-called Devices of the Media Gateways.
A Device consists of 24 (T1) or 31 (E1) termination and channel of 64 kbps.
- - Packet, ATM, CE Terminations - i.e. the circuits of the PTB, ATB, CTB Termination Boards. These terminations are static.
The attributes of Termination:
- logical - Termination (according to H.248 protocol)
- Epheremal Termination (H.248). Dynamic (IP) Termination exists only during the use.
It is assigned to a connection (context) with the "Add" command of H.248. Within an MGC domain we can terminate Virtual IP devices with this.
- Virtual IP device (Logical E1, IP termination, Termination ID.)
31 IP terminations for inter-domain semipermanent connections
Available termination is: interface related address + UDP port (4096...65535)
- Epheremal Termination (H.248). Dynamic (IP) Termination exists only during the use.
It is assigned to a connection (context) with the "Add" command of H.248. Within an MGC domain we can terminate Virtual IP devices with this.
- physical
- Termination Board
- Termination ID
- TeS, TS; MGC - Telephony Server - the control of the EIN/TSS VoIP MSSNs
The main function of the TS is the control (setup, release (Call Control Function)) speech (connections ).
TS has been created by the interconnection of an AXE exchange and an AXD.
Functional diagram of the TS:+-----+-----+ AXE |CCF |STD | CCF - Call Control Function +-+---+--+--+ STD - Special Telephony Devices Eth/ICP| MG-IC| ML - Mediation logic (AXE - H.248 conversion) +-+---+--+--+ MGWIC - Media Gateway Interconnect AXD |ML |MGWIC| Eth - Ethernet +-----+-----+ ICP - Internal Control Protocol (TRH) | | MG-IC - MG interconnect (E1 or STM1) H.248 ATM or IPThe main function of the AXE exchange is the call processing (call control) (CCF), while the main function of the AXD - controlled by the AXE - to control the switches of the MGWs (Connection Control (Media Gateway Control)) using a standardized protocol (ITU-T H.248.1). In AXD this task has been performed out by the ML Mediation Logic. Furthermore, ML converts AXE ICP messages into H.248 messages. Opcionally, the Gateway (MGWIC) implemented in AXD may connect the special telephone device (e.g. voice mail) of the AXE to the IP/ATM network.
There are no AXE exchange in the telecommunication test network of the department's laboratory its job has been carried out by a SUN WS and xxAxe emulator program running on it. - Testing (ATM)
- Call tracing
- Continuity check
- Performance monitoring
- Loop-back support
- TGW - Telephone gateway
- TIM - Trace Identifier Mismatch - Link alarm
- TRH - Transport Handler
- TSS (TSS 4.0) - Telephony Softswitch Solution - An example network of the manufacturer for the implementation of switched telephony service on the basis of IP bearer service model.
+----------+ | TS | +----------+ | | || +------ + +----------------+ | H.248 || | MGW ========== IP net ==== MGW - TU - Tributary unit - STM-1
- Type - type identifier of multiple object: EM, Device, Line Interface, Line Interface Sublayer, Link attributum, IP interface, IP address
- Tx - Transmit - adás
- V5.2 package
- VC
- Virtual Container - STM-1
- VC-12 - Virtual Container, level 1 (LOVC) (payload 2048 kbit/s), VC-12 interface index, VC-12 interface sublayer
- VC-4 - Virtual Container, level 4 (HOVC)
- Virtual Channel/Circuit (ATM)
- VCI - Virtual Channel/Circuit Identifier (ATM)
- Virtual host - An application address within the subnet of the underlying IP interface.
- Virtual IP device A virtual IP device is a representation of 31 channels in a group of IP UDP ports.
Each channel is represented by a Virtual IP termination. Virtual IP devices are only used for Inter-domain Leased Lines.
- Virtual IP termination A virtual IP termination is a termination in a virtual IP device. It must be configured by the operator to be used in an Inter-domain Leased Line or Inter-domain link. The Virtual IP termination is a physical termination.
- Voice & Telephony Services - Packet switched implementation of switched telephony service on ATM or IP network.
- VP, VPI - Virtual Path (ATM), VPI - Virtual Path Identifier
- VPB - Voice Processing Board (server type ET) - G.723, G.726, G.729 not implemented
- Voice Processing (VP) - It implements TDM/IP conversion in Voice & Telephony Services application. To the realization we need also a VPB, but to simpler conversion even the PTB Termination Board is able.
Configuration: in Switch Fabric/Voice Processing menu. (Profile 1...4)
Voice processing tools:- Jitter buffer
- A/u conversion
- Echo cancellation
- Tone handling
- Silence supression (needs Profile 2)
- Comfort noise
- Packet loss enhancement